North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO): Definition, Achievements and Criticism

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is a political and military alliance of 30 countries in Europe and North America. It was founded in 1949 with the goal of providing collective defense against the threat of Soviet aggression during the Cold War.
NATO’s fundamental principle is that an attack against one member is considered an attack against all members. To this end, NATO members have agreed to a system of collective defense, in which they agree to provide military and other support to any member that is the victim of an attack.
In addition to its core mission of collective defense, NATO has also played a role in crisis management, peacekeeping, and humanitarian operations around the world.
NATO is headquartered in Brussels, Belgium, and it is led by a Secretary General who is appointed by consensus of the member countries. The organization operates through a system of committees and bodies that are responsible for different areas of policy and operation.
NATO membership is open to any European or North American country that is able to contribute to the security and stability of the region and that is willing to accept the obligations of the NATO Treaty.
Achievements of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) has achieved a number of significant goals since its founding in 1949. Some of the most notable achievements of NATO include:
- Providing collective defense: NATO has helped to ensure the security and stability of its member countries by providing a system of collective defense against external threats.
- Promoting political and economic cooperation: NATO has played a role in promoting political and economic cooperation among its member countries, which has contributed to the growth and development of the transatlantic community.
- Supporting democratic transitions: NATO has supported democratic transitions in countries such as Kosovo, Afghanistan, and Iraq, through peacekeeping and stabilization missions.
- Responding to global challenges: NATO has also played a role in addressing global challenges such as terrorism and cyber threats, through the development of new capabilities and the deployment of troops and other resources.
- Enlarging the Euro-Atlantic community: NATO has played a role in the enlargement of the Euro-Atlantic community, by welcoming new member countries from Central and Eastern Europe.
Overall, NATO has contributed significantly to the security and stability of the Euro-Atlantic region, and it has helped to foster cooperation and solidarity among its member countries.
Criticism of NATO
There have been a number of criticisms of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) over the years. Some of the main criticisms of NATO include:
- Lack of burden sharing: Some critics have argued that NATO’s larger and more powerful member countries, such as the United States, bear a disproportionate share of the financial and military burden, while smaller and poorer member countries contribute less.
- Expanding too far: Some critics have argued that NATO has expanded too far and has taken on missions that are outside of its core area of responsibility, such as in Afghanistan and Libya.
- Provoking a new Cold War: Some critics have argued that NATO’s expansion and deployment of troops and military assets closer to Russia’s borders has exacerbated tensions with Russia and has contributed to a new Cold War.
- Undermining the United Nations: Some critics have argued that NATO has acted independently of the United Nations and has undermined the UN’s role as the primary international peace and security organization.
- Ignoring the views of non-member countries: Some critics have argued that NATO has ignored the views and interests of non-member countries, particularly in the Middle East and North Africa.
While NATO has achieved a number of significant goals, it has also faced criticism for its actions and policies.
Members countries in 2022
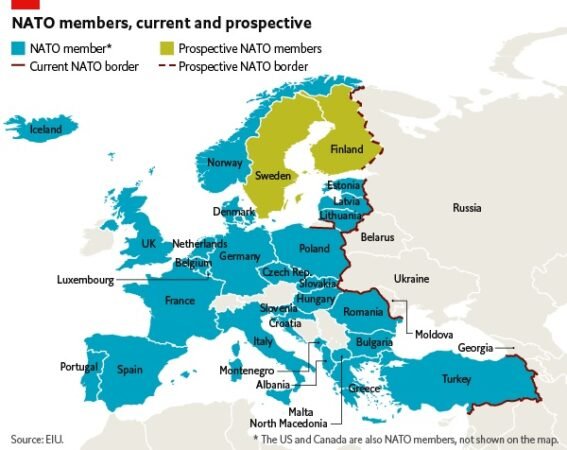
- Albania
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Canada
- Croatia
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- North Macedonia
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Turkey
- United Kingdom
- United States


















